Today we will be sharing the most asked Problem Management Interview Questions which can help the hiring managers as well as the candidates to have a good discussion of ITIL knowledge. Problem management’s main objective is to prevent incidents from happening and also minimize the count of incidents that can be prevented.

Table of Contents
Problem Management Interview Questions
What is a problem?
As per ITIL, a problem is defined as the underlying cause of one or more incidents. The problem requires investigation to find the causes and develop a long-term resolution, while creating a problem record we don’t know the underlying cause of it.
What is problem management?
It is the core component of ITSM frameworks, problem management to maintain the lifecycle of the problems and identify the cause of the incident on an IT service. The main objective is to eliminate the recurring incidents, minimize the impact of incidents, prevent problems and incidents from happening.
What are the different types of Problem Management?
There are two types of problem management.
- Reactive Problem Management.
- Proactive Problem Management.
What is reactive problem management?
The reactive problem management process is started once the issue is identified and the root cause was not identified and resolved in the incident management process. It is to analyze and deploy the long-term resolution for the issue. Example – Problem management will pick up one or more similar incidents and club them together to analyze which is the root cause is not identified in the incident lifecycle and prevent the recurring incidents.
ServiceNow Interview Questions
What is proactive problem management?
A proactive problem management process is in which ongoing activities are analyzed to prevent incidents from happening. Example – Problem management will analyze the existing logs, periodic audits, incident records and try to find a pattern or trend which is responsible for underlying issues.
Describe problem management process flow?
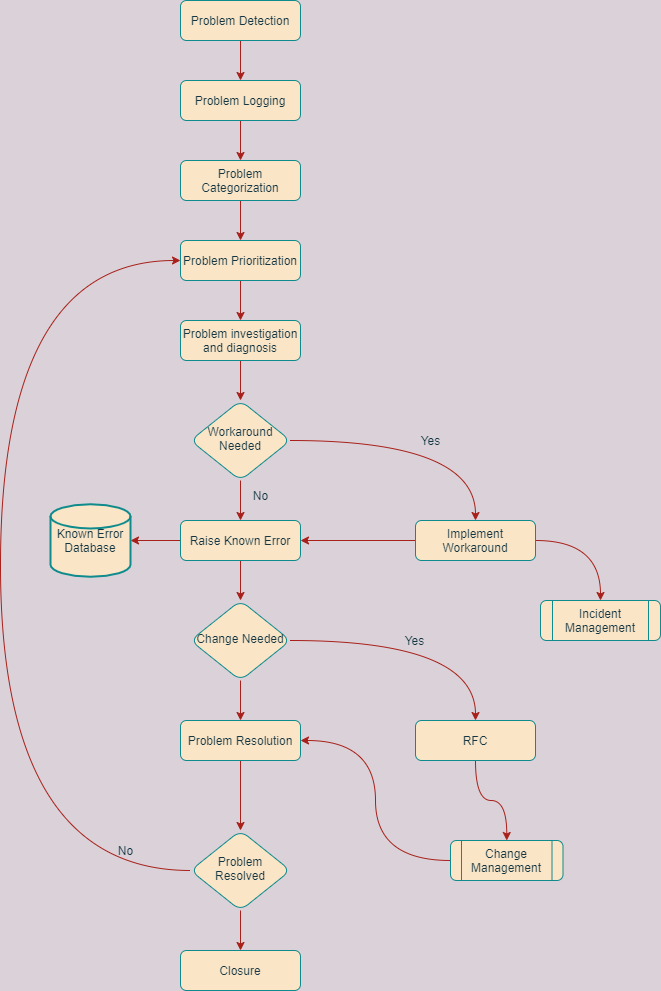
What’s the difference between an incident and a problem?
An incident is a single unplanned outage event that causes a disruption in an IT service. Incident management is focused on the restoration of service.
Problem is unknown cause by one or more potential incidents. The problem is focused on the underlying cause of an incident.
Incident Management Interview Questions
Can the priority of the problem be different from its incident?
Yes, priority can be different from its incident as there can be multiple incidents that occurred and which have caused a problem. So it depends on the impact of service failure and how critical it is to solve this problem to prevent recurring incidents.
What is Problem Categorization?
It is a step to identify which domain the problem is affecting, software, hardware, or security.
What is Problem Prioritization?
It is a step to measure whether it is a major problem that has a higher impact on the organization’s business.
What is the impact?
The impact measures the degree of service failure in simple words how many people are affected due to a problem or incident. For example – there can be a possibility mail server is not working for one user, so it will have a lower impact, whereas one department mail server is down will have a higher impact.
What is the urgency?
Urgency is the measure of how much important the service is to business. Example – There are critical services that can affect the delivery chain which will affect the profit and have a higher business loss.
What is an Error?
Any flaw which causes failure of one or more services or any other configuration item.
What is a known error?
A problem is identified and the root cause is documented with a workaround.
What is the root cause?
It is an original or underlying caused a service failure and then reported as an Incident or resulted in a problem.
What is Error Control?
Error control is responsible to manage known errors and responsible for removing/ resolving the known errors. Error control covers development, testing, deployment to live environment. The error control process is generally fed by two sources one is from real-time defects which are added in the know error database and the other is from pre-release known errors which are registered during developed or change activity.
What is CI?
CI is a component that needs to be managed to ensure the successful delivery of an IT service.
Give some examples of configuration items?
Services – Email, Printing.
Hardware – Server, Printer, Routers.
Software – Database, Applications, VM.
Devices – Laptop, Mouse, Monitor, Desktop.
What are the roles in Problem Management?
Problem Coordinator
Problem Analyst
Problem Manager
Problem Review Board
Process Owner
Service Owner
Technical Lead
Business Stakeholders
How are Problems related to Changes?
If a problem can be corrected there is a need for RFC (Request for a change) to move the solution between environment and audit it. Any change in the service or CI must go through the change process. Some of the corrections can be resolved without any change for example restarting or reset the device.
What is the value of problem management to the business?
The main objective of problem management is to prevent the recurrence of the incident and minimize the impact on the business. The value of problem management to businesses are
- Increased service productivity
- Increased service availability
- Improved service quality
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Reduced costs
- Reduced number of recurring incidents
- Decreased problem resolution time
- Empower team to find and learn underlying causes
- Promote continuous improvement
What are the KPI’s of Problem Management?
Measurement is an important aspect of any process, key performance indicators (KPI) are important to determine the effectiveness of a process. Problem management should have these KPI’s
- Problem reported by (person, group, organizational unit).
- Problem category (software, hardware).
- Root cause analysis report.
- Problem backlog.
- Problem exceeding the SLA.
- The average cost to manage a problem.
- Problem resolved in SLA.
- High priority problems.
- Average time to close a problem.
- The number of incidents resolved by a problem.
What are the benefits of IT problem management?
IT Problem management best practices?
Problem Solving Techniques Interview Questions
What is 5 Why Analysis?
what is the Cynefin framework?
What is Pareto analysis?
What is Kepner Tregoe Analysis?
What is Fish Bone Analysis?
Incident Problem Management Interview Questions
Can we raise a problem record without an incident?
Is it necessary for a problem manager to join a post-incident review?
How does proper ci classification in incidents help problem management?
What criteria do you consider before raising a problem record for an incident?
What do you do if the incident reoccurs when a related problem record was closed?
Change Problem Management Interview Questions
How change management is related to problem management?
When RFC is required in the problem management lifecycle?
Can a problem fix result in an emergency change?
Does all problem resolution is implemented through change?
Please let us know if any problem management interview questions you like to ask other candidates or they have been asked to you which may help other job seekers.